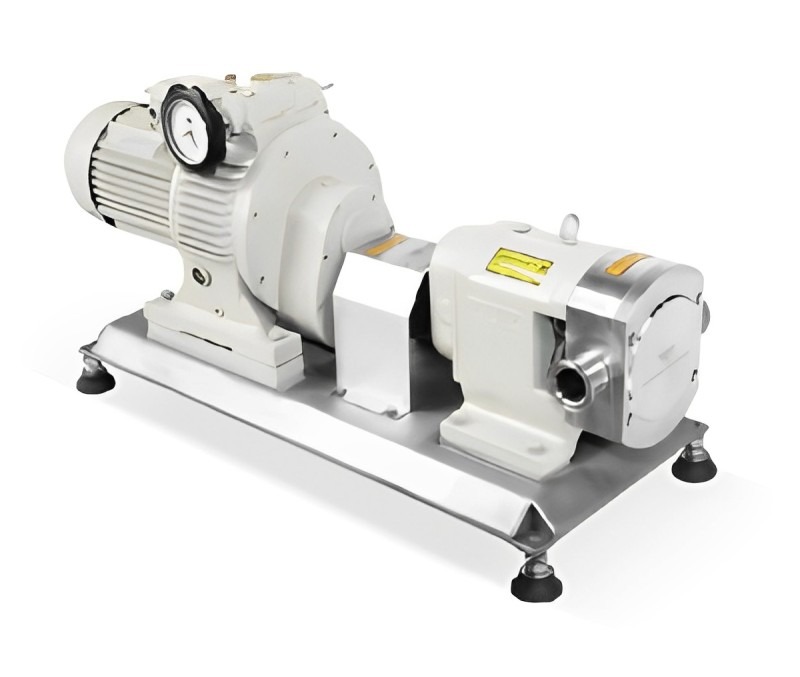
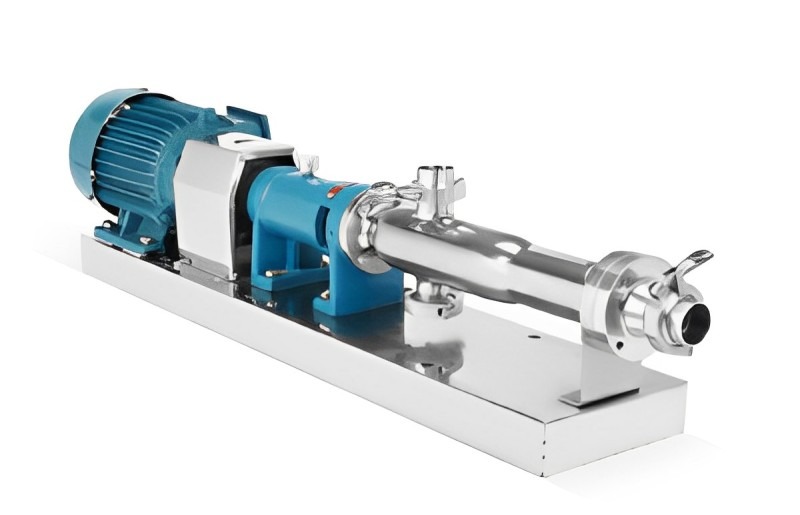
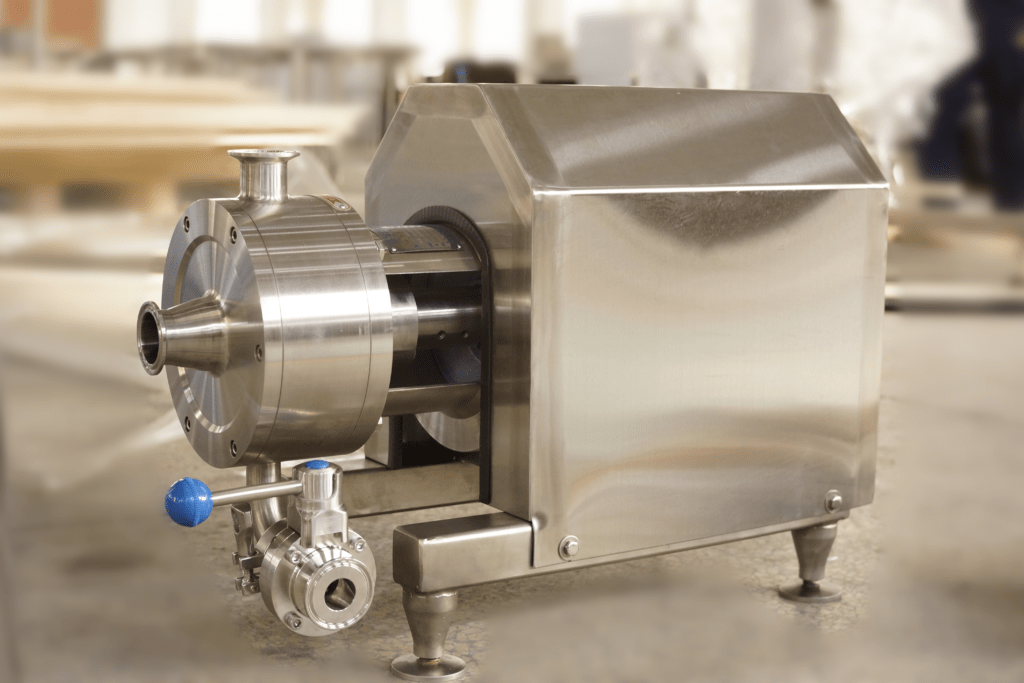
Emulsion pump is a special type of pump specifically used in the stirring and mixing process of emulsified liquids. It is mainly used to disperse immiscible liquids such as oil and water, under the action of high-speed shear and impact force, to promote the mutual dispersion of immiscible liquids and form small and uniform particles, forming emulsions.
-
Working principle of emulsion pump
The shear and impact forces generated by the high-speed rotating impeller cause the dispersion between the oil and water phases to break apart and redisperse, resulting in the formation of a small and uniformly distributed emulsion.
-
Emulsification pumps are commonly used in the food industry, cosmetics industry, pharmaceutical industry, chemical industry, and other fields to prepare emulsified sauces, emulsions, emulsifiers, dye emulsions, and other products.
-
The main components of an emulsion pump include:
(1) Pump body: The outer shell of an emulsification pump, usually made of stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials.
(2) Impeller: The rotating component inside an emulsion pump, composed of multiple blades. The impeller generates shear and impact forces through high-speed rotation, promoting liquid emulsification.
(3) Import pipeline: used to feed the mixture to be emulsified into the emulsification pump. Imported pipelines are usually of appropriate size and shape to ensure smooth fluid entry into the pump body.
(4) Export pipeline: used to discharge emulsified liquid from the emulsification pump. The outlet pipeline is usually connected to an emulsifier or other equipment for further processing or use of emulsion.
-
Emulsion pumps usually have the following characteristics and applications:
(1) Structural features: Emulsification pumps have different structural forms, commonly including centrifugal pumps, propulsion pumps, submersible pumps, etc. Emulsification pumps usually have high-speed rotating impellers or rotors to generate high shear force and mixing force, so as to achieve the formation of lotion.
(2) Emulsification effect: The centrifugal force and fluid pressure generated by high-speed rotation of the emulsification pump disperse immiscible liquids and form small droplets. An emulsification pump can emulsify oil and water (or other liquids) into a stable emulsion, improving solubility and mixing efficiency.
(3) Application field: Emulsification pumps are widely used in the emulsification process of industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, cosmetics, etc. In the food industry, emulsification pumps are often used for oil-water emulsification, dairy emulsification, jam emulsification, etc; In the chemical industry, emulsion pumps are often used to emulsify lotion, coatings, adhesives and other liquids.
(4) Design requirements: The emulsification pump needs to be designed and selected based on specific process requirements and product characteristics. Due to the high shear and stirring forces generated by the emulsification pump during the emulsification process, it is necessary to consider factors such as the pump’s wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and material selection.
-
The advantages of an emulsification pump mainly include:
(1) Good homogeneous emulsification effect: The emulsification pump can disperse liquid substances into smaller particles, making the substances more delicate and uniform, thereby improving product quality and taste.
(2) High production efficiency: The emulsification pump can complete a large amount of substance emulsification in a short period of time, thus significantly improving production efficiency.
(3) Easy to operate: The emulsification pump is easy to operate, and only a simple operation is needed to complete the homogeneous emulsification of the product.
(4) Wide applicability: Emulsification pumps can homogenize and emulsify different types of substances, making them widely used in fields such as food, medicine, and cosmetics.
(5) Simple structure: The emulsification pump has a relatively simple structure and is easy to maintain and clean.
(6) Smooth operation: The horizontal plunger reciprocating pump runs smoothly with stable flow rate, and is not prone to large-scale fluctuations or blockages.
(7) High mixing efficiency: The emulsification pump can effectively mix and evenly disperse multiple materials.
-
The disadvantages of emulsification pumps include:
(1) High maintenance cost: If the internal parts of the emulsification pump are damaged, it may require higher repair costs and time.
(2) Restricted by the pipeline system: The normal operation of the emulsification pump may be affected by the pipeline system, such as pipeline blockage or leakage.
(3) High operational requirements: The operation of emulsification pumps requires professional knowledge and skills, and improper operation may cause equipment damage or affect product quality.
(4) High noise: The emulsification pump may produce significant noise during operation.
(5) There are limitations to the transportation of materials: there may be certain limitations in the transportation of materials by emulsification pumps, such as viscosity, particle size, etc.
-
What is the difference between an emulsification pump and a mixer?
There are obvious differences between emulsification pumps and mixers in terms of principle, application scope, structure, appearance, and advantages and disadvantages.
(1) Principle: The emulsification pump disperses, shears, and homogenizes materials through homogeneous emulsification, while the mixer completes mixing by quickly stirring the materials.
(2) Application scope: Emulsification pumps are mainly used for materials with high viscosity, high concentration, easy solidification or layering, while mixers are suitable for materials that are easy to mix.
(3) Equipment structure: The gap between the rotor and stator of the emulsification pump is very small, while the blades of the mixer are usually longer.
(4) Appearance: Emulsification pumps are usually pipeline or vertical structures, while mixers are generally desktop or vertical structures.
(5) Advantages and disadvantages: The advantages of an emulsifier lie in its good mixing effect, stable performance, good emulsification effect, and better quality achieved compared to a mixer. At the same time, it can also achieve heating, cooling, and other operations. The advantages of mixers lie in their low cost, simple structure, easy maintenance, low impact force, and wide range of suitable mixing materials. Some mixers can mix solids and powders.
-
How to choose an emulsification pump
(1) Determine requirements: Firstly, clarify your own requirements, including the application field of the emulsification pump, the properties of the processed materials, production scale, etc. This will help narrow down the selection range and find the most suitable emulsification pump.
(2) Understand the market: Collect information about the emulsification pump market, and understand the differences in performance, price, and other aspects among different brands and models. Market research can be conducted by consulting professional magazines, attending industry exhibitions, consulting relevant industry experts, and other means.
(3) Performance comparison: Based on the collected information, compare the performance parameters of different emulsification pumps, such as flow rate, pressure, power, etc. Ensure that the selected emulsification pump can meet production needs and has high efficiency.
(4) Considering durability: Emulsification pump may be subject to wear and tear during use, so it is necessary to choose emulsification pumps made of wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials to ensure their service life and stability.
(5) Consider maintainability: Choose an emulsification pump that is easy to disassemble, clean, and repair to reduce maintenance costs and downtime.
(6) Choose a suitable supplier: Collaborate with reputable and after-sales service providers to ensure the purchase of high-quality and reasonably priced emulsification pump.
(7) Reference user feedback: Refer to other users’ evaluations and suggestions on the emulsification pump to understand the actual use of the equipment and potential issues.
(8) Considering energy efficiency: On the premise of meeting production needs, choose emulsification pump with higher energy efficiency to reduce energy consumption and operating costs.
(9) Customized requirements: If there are special requirements, we can consider customizing emulsification pump to meet specific process requirements and production environments.
(10) Trial operation and acceptance: Before purchasing the emulsification pump, conduct a trial operation and acceptance to ensure that the equipment performance meets the expected requirements.
(11) Following the above suggestions and considering multiple factors comprehensively can help you choose a suitable emulsion pump.